Background
About the Project
In 2016, the USDOT launched its Connected Vehicle Project, aiming to spur early connected vehicle (CV) tech deployment, measure deployment benefits, and resolve deployment issues to help the nation transition into a more connected future. Three pilot sites were chosen for this pilot: Wyoming, New York City, and Tampa.
NYC
The New York City Connected Vehicle Pilot Program (NYC CVPD), led by the New York City Department of Transportation (NYCDOT), will use vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) DSRC communications to improve safety through the reduction of vehicle and pedestrian crashes, injuries, and fatalities.
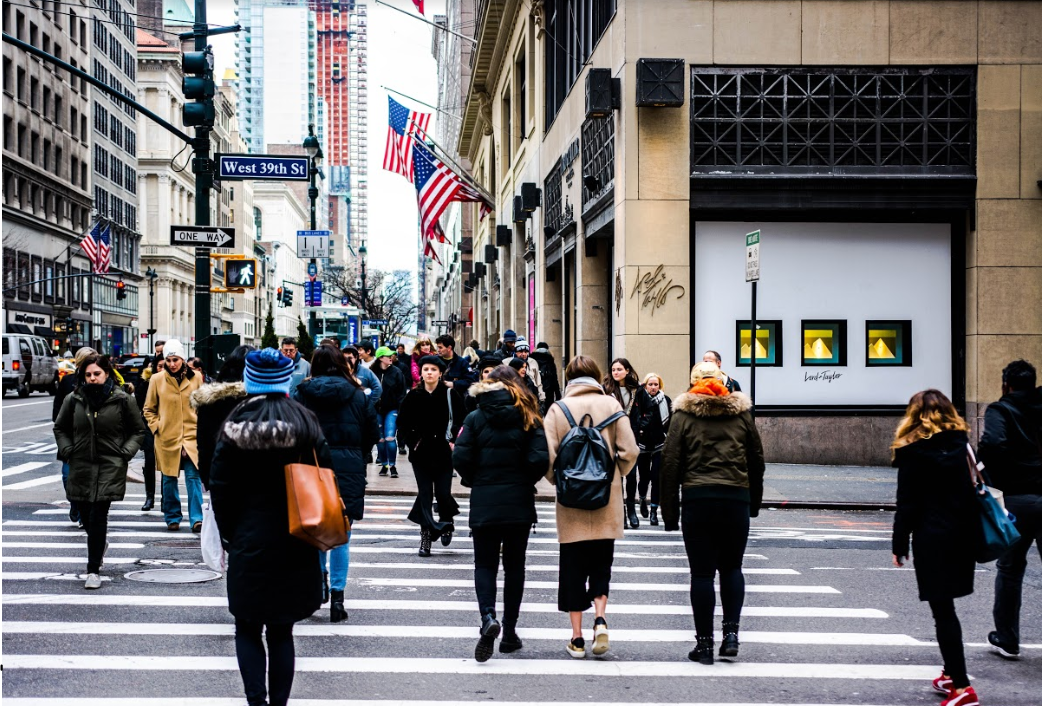

The Research
Project Briefs
NYCCVPD
The Research
Results & Evaluation
NYCCVPD
CV technologies also have the potential to improve accessibility for disadvantaged populations by providing timely and efficient traveler information about the real time availability of transportation options, as well as non-recurrent congestion that can cause major delays at most unexpected times.
Kaan Ozbay Director, C2SMARTLessons Learned
WEBINARS
WEBINARS
- October 7
- October 25
- November 9
- November 16
Sponsored by the U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT), the Connected Vehicle Pilot Deployment (CVPD) Program which piloted the technology in three sites, New York City (NYC), Wyoming, and Tampa, is a national effort to deploy, test, and operationalize cutting-edge in-vehicle, mobile and roadside technologies and enable multiple connected vehicle (CV) safety and mobility applications. According to the National Highway Transportation Safety Administration (NHTSA), speeding was a factor in more than one in four deaths and human factors were the critical cause in about 94% of all crashes. The NYC CVPD has undertaken connected vehicle technology as another tool that could be used to help further the city’s Vision Zero goals. The experimental design included equipping 3,000 vehicles with Aftermarket Safety Devices (ASD) for vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I), and pedestrian applications. This seminar will present the data cleaning, evaluation methodology, performance measurement, and safety evaluation results of the 12 CV safety applications that was conducted during the Phase 3 operational phase of the deployment.
Speaker
 Dr. Di Yang is a tenure track Assistant Professor in the Department of Transportation & Urban Infrastructure Studies at Morgan State University. His research focuses on developing novel statistical and data-driven methods at the intersection of transportation safety, connected and autonomous vehicles, human factors, policy analysis, and shared mobility. His research contributions have led to 27 publications in various journals and conferences, featuring 11 first-author papers, and recognized by the Institute of Transportation Engineers (ITE) Northeastern District Daniel B. Fambro Student Paper Award in 2021.
Dr. Di Yang is a tenure track Assistant Professor in the Department of Transportation & Urban Infrastructure Studies at Morgan State University. His research focuses on developing novel statistical and data-driven methods at the intersection of transportation safety, connected and autonomous vehicles, human factors, policy analysis, and shared mobility. His research contributions have led to 27 publications in various journals and conferences, featuring 11 first-author papers, and recognized by the Institute of Transportation Engineers (ITE) Northeastern District Daniel B. Fambro Student Paper Award in 2021.
 Dr. Jingqin (Jannie) Gao, completed her Ph.D. in Transportation Planning and Engineering at NYU Tandon, and is currently working as a lead researcher at C2SMART University Transportation Center funded by US Department of Transportation. She studied Science and Technology of Optical Information and received her B.S. from Tongji University and her M.S in Transportation Planning and Engineering from New York University. Her research interests lie in big data and artificial intelligence solutions for transportation, emerging technologies such as connected vehicles, traffic simulation modeling, parking management and transportation economics. Before joining NYU, she worked for the New York City Department of Transportation on modeling and data analysis to support the agency’s internal planning and technical review processes. Jingqin plays a leadership role both within her research group and for the larger NYU Tandon community, serving as the president of the student chapters of the Institute of Transportation Engineers and the Intelligent Transportation Society.
Dr. Jingqin (Jannie) Gao, completed her Ph.D. in Transportation Planning and Engineering at NYU Tandon, and is currently working as a lead researcher at C2SMART University Transportation Center funded by US Department of Transportation. She studied Science and Technology of Optical Information and received her B.S. from Tongji University and her M.S in Transportation Planning and Engineering from New York University. Her research interests lie in big data and artificial intelligence solutions for transportation, emerging technologies such as connected vehicles, traffic simulation modeling, parking management and transportation economics. Before joining NYU, she worked for the New York City Department of Transportation on modeling and data analysis to support the agency’s internal planning and technical review processes. Jingqin plays a leadership role both within her research group and for the larger NYU Tandon community, serving as the president of the student chapters of the Institute of Transportation Engineers and the Intelligent Transportation Society.

 Dr. Kaan M.A. Ozbay joined Department of Civil and Urban Engineering and Center for Urban Science and Progress (CUSP) at NYU in August 2013. Since 2017, Ozbay has been the Founding Director of the C2SMART Center (Tier 1 UTC funded by USDOT). He is also Global Network Professor of Civil and Urban Engineering, NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) and Global Network Professor of Engineering and Computer Science, NYU Shanghai (NYUSH). Ozbay was a tenured full Professor at the Rutgers University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. He joined Rutgers University as a tenure track Assistant Professor in July, 1996. In 2008, he was a visiting scholar at the Operations Research and Financial Engineering (ORFE) Department of Princeton University. Ozbay is the recipient of the prestigious National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER award.
Dr. Kaan M.A. Ozbay joined Department of Civil and Urban Engineering and Center for Urban Science and Progress (CUSP) at NYU in August 2013. Since 2017, Ozbay has been the Founding Director of the C2SMART Center (Tier 1 UTC funded by USDOT). He is also Global Network Professor of Civil and Urban Engineering, NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) and Global Network Professor of Engineering and Computer Science, NYU Shanghai (NYUSH). Ozbay was a tenured full Professor at the Rutgers University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. He joined Rutgers University as a tenure track Assistant Professor in July, 1996. In 2008, he was a visiting scholar at the Operations Research and Financial Engineering (ORFE) Department of Princeton University. Ozbay is the recipient of the prestigious National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER award.
This roundtable discussion focuses on these recently completed connected vehicle pilots and the lessons learned. Our panelists feature practitioners, decision-makers, and researchers involved in CV deployments and leading the way for their wide-scale adoption.
Sisinnio Concas serves as Program Director at the Center for Urban Transportation Research (CUTR) and Research Associate Professor the University of South Florida (USF) College of Engineering. He has performed numerous research projects for the U.S. Federal Transit Administration, Federal Highway Administration, the Florida Department of Transportation, state and local transportation authorities. Dr. Concas leads the Performance Measurement Evaluation and Support of the Tampa CV Pilot Deployment.
Dr. Mohamad Talas is the Deputy Director of ITS System Engineering, New York City Department of Transportation. He brings long standing career experience in traffic engineering and continue with over 27 years in Traffic Engineering and Operation experience in New York City Department of Transportation. He currently serves as the Director for the NYC Department of Transportation ITS project Management, Research and Development where he supervises the Intelligent Transportation System projects and initiatives in New York City. He has earned his PhD in Transportation Planning and Engineering at NYU -Poly University, Master degrees in Transportation, Planning and Engineering and a Masters in Electrical Engineering from Fairleigh Dickinson University.
Billy Chupp is a data analyst and engineer at the U.S. Department of Transportation’s Volpe Transportation Systems Center in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Mr. Chupp most recently served as the technical lead on Volpe’s independent safety evaluation effort for the three connected vehicle pilot programs in New York City, Tampa, and Wyoming, and continues to support the ITS JPO on data documentation and strategy efforts within the connected vehicle space and beyond.
Dr. Karl Wunderlich holds a joint appointment at Noblis in Washington, DC., serving as both is the Director of the Surface Transportation Division and the Director of the Noblis Autonomous Systems Research Center. He is a published author and patent-holder in orchestrated autonomy, which leverages blockchain to create efficient and collision-free path planning among heterogenous, unfamiliar, and autonomous machines. Dr. Wunderlich holds a Ph.D. in Operations Research from the University of Michigan.
Dr. Kaan Ozbay is a Professor at New York University’s Tandon School of Engineering, and Director of C2SMART Center, a Tier 1 USDOT University Transportation Center. Dr. Ozbay served as Principal Investigator (PI) of the NYU/C2SMART team as part of the NYCDOT-led New York City Connected Vehicle Pilot, under USDOT’s Connected Vehicle Pilot Program. He joined NYU’s Department of Civil and Urban Engineering and Center for Urban Science and Progress (CUSP) in August 2013, and is also Global Network Professor of Civil and Urban Engineering, NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) and Global Network Professor of Engineering and Computer Science, NYU Shanghai (NYUSH).
Jingqin (Jannie) Gao completed her Ph.D. in Transportation Planning and Engineering at NYU Tandon, where she works with C2SMART Director Kaan Ozbay. She studied Science and Technology of Optical Information and received her B.S. from Tongji University in China and her M.S in Transportation Planning and Engineering from New York University. Her research interests lie in offline and real-time simulation modeling, big data and machine learning approach for transportation, and transportation economics. She also worked for the New York City Department of Transportation on modeling and data analysis to support the agency’s internal planning, technical review processes and coordinated with external agencies on regional projects since 2012. Jingqin is the former president of NYU’s joint Institute of Transportation Engineers (ITE) and The Intelligent Transportation Society of America (ITS) Student Chapter during 2018-2019, through which she organized various company visits, tech talks, women in transportation events and the 2019 ITE Northeastern District Traffic Bowl.









Technologies like this can and should be harnessed to help ensure that New York City is navigable, accessible, and safe for all pedestrians,” says C2SMART’s lead researcher on the PED-SIG project, Dr. Jingqin Gao. “With some refinement and iteration, CV apps could enable New Yorkers with vision disabilities to be as mobile and independent as New Yorkers with perfect vision.
Jingqin Gao Senior Research Associate, C2SMART