According to the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), work zone fatalities at road construction projects account for up to 3% of all workplace fatalities in a given year, and the primary causes are runovers/backovers, collisions, and caught in-between mobile equipment. One of the main proactive approaches adopted by construction companies to prevent these incidents is safety training courses, which are designed to help increase workers’ awareness of hazards around the job sites and take timely actions to avoid injuries. However, work zone safety knowledge from training courses is not enough to change the level of vigilance of workers, which is easily affected by factors such as fatigue or environmental distractions. With the development of wearable technologies, an increasing number of research studies have been exploring the feasibility of using wearable sensors to detect workers’ attention and vigilance towards job site hazards. However, merely measuring workers’ awareness of hazards is not sufficient. There is still a need to understand key parameters that impact worker and driver behaviors regarding received alarms/warnings/notifications and design notification systems that are calibrated for the optimal time, frequency, and modality to push information on potential hazards at work zones.
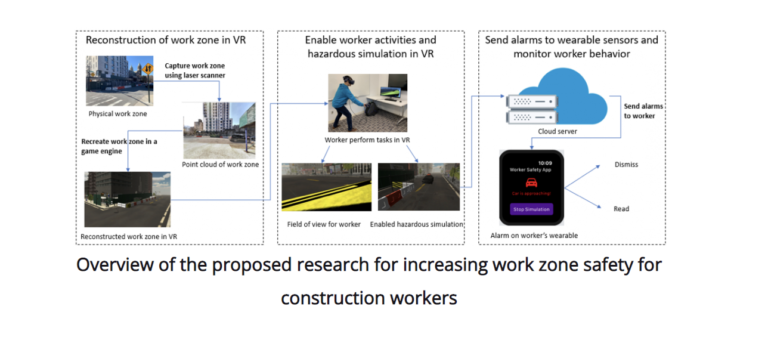
With the goal of reducing the number of injuries and fatalities, this project aims to understand the key parameters (e.g., work zone location characteristics, personal vigilance levels, types of construction work) that play roles in achieving responsive behaviors in workers. Key questions this research will address include in what conditions people ignore or respond to warnings, how notification systems can be calibrated for getting responsive actions from workers, and what modalities, frequencies, and timings of pushing notifications are most effective. Through wearable sensors and realistic representations of work zones in virtual reality, we plan to collect worker behavioral and physiological (heart rate) responses to warnings issued under various realistic scenarios and various warning mechanisms.